| Welcome, Guest |
You have to register before you can post on our site.
|
| Online Users |
There are currently 552 online users.
» 0 Member(s) | 541 Guest(s)
Ahrefs, Amazon, Bing, Bytespider, Claude, Google, OpenAI, Petalbot, Semrush, Seznam, Trendiction
|
|
|
| 850E Seat Replacement Issues and Solutions |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:41 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Overview of the Problem
The 850E bulldozer is a versatile piece of machinery widely used in construction and heavy-duty earthmoving tasks. However, over time, the comfort and functionality of the 850E's seat can degrade, leading to discomfort during long operating hours. This has prompted many operators to replace the seat to improve comfort and productivity. This article explores common issues with the 850E seat and offers solutions for replacing it.
Common Seat Replacement Issues
- Seat Damage or Wear
After prolonged use, the original seat in the 850E bulldozer can experience wear and tear. The material may degrade, resulting in cracks, wrinkles, or even structural issues with the seat frame. These issues can reduce the overall comfort and support for the operator, impacting their ability to work effectively for extended periods.
- Malfunctioning Seat Adjustment Mechanism
Another common issue is a malfunctioning seat adjustment system. Over time, the mechanisms that control seat height, tilt, and fore-and-aft movement may fail. This can be caused by damage to the mechanical components or issues with hydraulic systems (if applicable), which makes it difficult to adjust the seat to a comfortable position.
- Compatibility Issues When Replacing the Seat
When replacing the seat in the 850E, compatibility with the machine’s existing mounting system can be a concern. Many replacement seats on the market may not fit perfectly with the original mounting points, requiring additional modifications or adapters to ensure proper installation.
Seat Replacement Recommendations
- Choose the Right Seat
The first step in replacing the 850E seat is to ensure that the new seat is compatible with the machine’s size and installation requirements. There are various options for bulldozer seats available on the market, and it's important to select one that offers good support, adjustability, and comfort suited to the operator’s needs.
- Check the Adjustment Mechanism
When replacing the seat, ensure that the adjustment mechanisms are fully functional. If the original seat’s adjustment features were malfunctioning, inspect the adjustment controls, air suspension, or hydraulic systems to ensure the new seat works smoothly and provides the needed flexibility.
- Seat Installation
During installation, ensure that the new seat aligns with the original mounting points. If the mounting points do not match, consider using an adapter to make the installation easier. Be sure to securely fasten all bolts to prevent any instability or loosening during operation.
Conclusion
Replacing the seat in the 850E bulldozer can significantly enhance the operator’s comfort and efficiency. By selecting the right replacement seat, ensuring proper adjustment functionality, and making sure the seat fits correctly, you can address issues like seat wear and adjustment failure. Compatibility is a key factor in the replacement process, so ensuring the new seat matches the bulldozer’s installation system is crucial for a smooth and secure replacement.
|

|
|
| Analysis and Solutions for 311B Excavator Monitor Problems |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:41 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
When using the 311B excavator, the monitoring system may experience malfunctions, leading to issues such as failure to display operational parameters or incorrect readings. These problems can affect the equipment's functionality and reduce operational efficiency. Therefore, diagnosing and resolving monitor system issues promptly is essential for maintaining smooth operations.
Common Issues and Causes
- Blank or No Display on the Screen
A blank or non-functional display is one of the most common problems with the monitoring system. This is often caused by power supply issues, loose cable connections, or faults in the display unit itself.
- Abnormal Monitoring System Parameters
If the displayed operational parameters (such as oil temperature, hydraulic pressure, etc.) are inaccurate, this may be due to sensor failure or electrical connection issues, causing incorrect data transmission.
- Touchscreen Malfunction
In some 311B machines, the touchscreen may become unresponsive or slow to respond after prolonged use or due to external factors, affecting the convenience of the operator.
- Monitoring System Fails to Start
Occasionally, the monitoring system may fail to start, with the display screen not loading into the operational interface. This is usually due to faults in the electronic control system or missing startup signals.
Troubleshooting and Solutions
- Check Power Supply and Cable Connections
Start by verifying that the power supply to the equipment is functioning correctly and ensure that all cable connections, especially between the display and the main control unit, are secure. If any connections are loose or damaged, they should be reconnected or replaced.
- Inspect Monitor System Fuses
A blown fuse in the monitoring system can cause it to fail. Check all fuses related to the monitor system and replace any that are damaged.
- Check Sensors and Data Transmission
If operational parameters appear abnormal, the issue may lie with a faulty sensor or electrical connection. Inspect all sensors connected to the monitoring system to ensure they are functioning correctly and transmitting accurate data.
- Restart or Reset the Monitoring System
Sometimes, restarting or resetting the monitoring system can resolve temporary glitches. Turn off the equipment, wait for a few minutes, and then restart it to see if the issue is resolved.
- Inspect the Electronic Control System
If the monitoring system fails to start, the issue may be within the electronic control unit. Ensure that the electronic control system is functioning properly and that the startup signal is being transmitted correctly.
Conclusion
Common issues with the 311B excavator’s monitoring system include blank displays, abnormal parameters, touchscreen malfunctions, and failure to start. By troubleshooting power connections, sensors, fuses, and the electronic control system, these issues can be effectively resolved. This ensures the monitoring system operates properly, improving the equipment’s performance and ease of use for the operator.
|

|
|
| CAT 140 Elevating System Issues and Solutions |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:39 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
The CAT 140 grader is widely used in road construction and earthmoving projects. As a powerful and precise machine, it provides exceptional elevating and cutting functionality, making it a central piece of equipment for many construction tasks. However, some users report issues with the elevating system during operation, which can impact the performance and reliability of the machine.
Common Elevating System Issues
- Unstable Elevation Function
Some CAT 140 users have experienced unstable elevating functions. This can manifest as uneven blade elevation or an inability to maintain the set height. This issue is often related to insufficient hydraulic pressure, contaminated hydraulic oil, or faulty hydraulic cylinders.
- Hydraulic Pressure Irregularities
The hydraulic system is critical for the elevating function on the CAT 140. Hydraulic system issues, such as sluggish lifting, unresponsive movements, or hydraulic oil leaks, are common. These problems typically result from a damaged hydraulic pump, ruptured or leaking hydraulic hoses, or poor-quality hydraulic oil.
- Difficulty Adjusting Blade Angle
Precise blade angle adjustments are crucial for accurate operation. Some operators have reported difficulty in adjusting the blade angle smoothly between required positions. This issue is usually related to a malfunctioning hydraulic valve, control system failure, or excessive buildup of hydraulic oil.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Recommendations
- Inspect the Hydraulic System
If the elevating function is unstable, the first step is to check the hydraulic system’s pressure and oil level. Ensure that the hydraulic oil is not contaminated, and inspect the hydraulic pump and hoses for any leaks. If any issues are found, replace or repair damaged components and change the hydraulic oil.
- Check Hydraulic Pressure
Inspect the hydraulic pressure to ensure it is within normal operating ranges. If pressure is insufficient, examine the hydraulic pump to verify that it is working properly or if the pressure valve needs adjustment. Also, ensure that the hydraulic oil quality is up to specification to prevent system malfunctions due to poor oil quality.
- Adjust Blade Control System
For issues with adjusting the blade angle, check the control valves and adjustment systems for faults. Clean and maintain the hydraulic control system, ensuring that all connections are functioning correctly. If excess hydraulic oil has accumulated, drain the excess to prevent issues with control.
Conclusion
The CAT 140 elevating system is a crucial tool for completing precise grading tasks, but it can experience common hydraulic issues such as unstable elevation, irregular hydraulic pressure, and difficulty adjusting the blade angle. Regular checks of the hydraulic system, adjustments to hydraulic pressure, and proper maintenance of the blade control system can effectively resolve these issues, ensuring the CAT 140 operates smoothly and efficiently, improving productivity on the job site.
|

|
|
| Electronic Control Valves: Operation and Troubleshooting |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:39 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Electronic Control Valves (ECVs) are widely used in modern heavy machinery, particularly in hydraulic systems, to control the flow direction, pressure, and speed of fluids. With technological advancements, ECVs have replaced traditional mechanical control valves, offering more precise and efficient operation. However, like any system, they can experience common faults that require timely troubleshooting and repair.
Working Principle of Electronic Control Valves
Electronic Control Valves use electrical signals to control the movement of the valve spool, thereby regulating the flow of hydraulic fluid. Typically, the control system receives input from the operator (e.g., throttle, joystick), converts it into an electronic signal, and sends it to the solenoid valve to control the flow rate or pressure.
- Signal Transmission
ECVs rely on electronic signals to regulate the hydraulic fluid pathways. The Electronic Control Unit (ECU) processes the data from sensors, converts it into control signals, and sends these signals to the solenoid valves to regulate the flow or pressure.
- Precise Control
One of the advantages of ECVs is their high level of precision. By adjusting the strength and frequency of the electronic signals, the control system can finely tune the flow rate and pressure for optimal performance.
Common Issues and Causes
- Signal Distortion or Loss
ECVs require accurate signal input to function properly. If the signal transmission is disrupted or lost, it can cause the valve to malfunction, affecting the hydraulic system’s functionality.
- Solenoid Valve Failure
As the core component of an ECV, the solenoid valve can fail due to overheating, wear, or electrical faults. If the solenoid valve fails, hydraulic fluid cannot flow properly, and the system will not operate as expected.
- Sensor Issues
Sensors used to monitor pressure, flow, or position in the hydraulic system can fail, preventing the ECV from receiving accurate data input. This can result in slow or inaccurate system responses.
- Electronic Control System Failure
The ECV relies on a stable electronic control system to function properly. If there is an issue with the power supply or the control unit, it can lead to the valve failing to operate as intended.
Troubleshooting and Solutions
- Check the Electronic Signals
Use diagnostic tools to check the signal transmission in the electronic control system. If there is signal loss or distortion, inspect the wiring, connectors, and signal sources for issues.
- Inspect the Solenoid Valve
Check the solenoid valve’s electrical connections to ensure it is working correctly. If the valve is faulty, it may need to be replaced or repaired.
- Examine the Sensors
Regularly check the sensors in the hydraulic system to ensure they are providing accurate pressure and flow readings. If a sensor is malfunctioning, it may need to be replaced or recalibrated.
- Inspect the Electronic Control Unit
If there are problems with the control system, first check the electronic control unit and its power supply to ensure they are functioning correctly. If needed, repair or replace the components.
Conclusion
Electronic Control Valves improve the precision and efficiency of hydraulic systems but may experience issues such as signal distortion, solenoid valve failure, sensor problems, or control system malfunctions. Regular inspection of the signal transmission, solenoid valve, sensors, and control system can help ensure optimal performance and prevent production downtime caused by system failures.
|

|
|
| Common Issues and Solutions for the CASE 420B Backhoe |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:38 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Overview of the CASE 420B Backhoe
The CASE 420B backhoe is a versatile piece of machinery widely used in construction and civil engineering. It combines digging, lifting, and loading functions, making it a popular choice in the field. However, like many heavy-duty machines, the CASE 420B can experience a range of common issues, particularly with extended use over time.
Common Issues and Causes
- Hydraulic System Problems
The hydraulic system is one of the most crucial components of the backhoe. In the CASE 420B, issues such as insufficient hydraulic pressure or hydraulic oil leakage are frequent. These problems are often caused by damage to the hydraulic pump, valves, or hoses. If the hydraulic system fails, the machine’s movements become sluggish or unstable, and in severe cases, it may not function at all.
- Engine Performance Degradation
Over time, the engine of the CASE 420B may experience a decline in performance. Symptoms include difficulty starting, slow acceleration, or irregular engine power. These issues are often linked to carbon buildup in the fuel system, a clogged air filter, or damaged fuel injectors. Regular cleaning or replacement of the air filter and fuel injectors is an effective solution to address these problems.
- Transmission Issues
The transmission is another vital component of the CASE 420B backhoe. When the transmission malfunctions, common symptoms include difficulty shifting gears and sluggish acceleration. These issues are typically caused by worn gears, a malfunctioning hydraulic system, or insufficient transmission fluid.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance Recommendations
- Hydraulic System Checks
Regularly inspect the quality and level of hydraulic oil, ensuring that the hydraulic pump and hoses are free from leaks. If hydraulic pressure is low or there is oil leakage, replace damaged components and clean any contaminants from the system.
- Engine Maintenance
Perform routine checks and clean the engine’s air filter, maintain fuel system cleanliness, and replace fuel injectors as needed. If the engine is slow to start or accelerate, check the fuel system for issues, clean, and replace necessary parts.
- Transmission Maintenance
For transmission issues, begin by checking the fluid level and condition. If the transmission fluid is low or contaminated, replace it immediately. Inspect the gears for wear and tear, and repair or replace them as necessary.
Conclusion
The CASE 420B backhoe may encounter common issues such as hydraulic system failures, engine performance decline, and transmission problems. Through regular inspections, maintenance, and timely repairs, these issues can be identified and resolved, significantly extending the life of the machine and ensuring it operates smoothly.
|

|
|
| Analysis and Solutions for Komatsu D20A-5 Engine Cylinder Head Issues |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:38 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Overview of the Problem
The engine cylinder head of the Komatsu D20A-5 Crawler Dozer often experiences common issues such as damage, coolant leakage, or poor compression. These problems can significantly affect the engine's performance and, if left unaddressed, may result in the engine failing to start or losing power, requiring prompt inspection and repair.
Common Issues and Causes
- Cylinder Head Damage
Over time, the cylinder head can crack or become damaged due to overheating or excessive load. Such damage can lead to loss of compression, impacting the engine's operation.
- Coolant Leakage
Cracks or damage to the cylinder head may result in coolant leakage. This can cause the engine to overheat, potentially leading to more severe engine damage if not addressed.
- Poor Compression
If the cylinder head’s sealing is inadequate, it may cause poor compression, which can affect engine startup and power output. Poor sealing is often due to worn cylinder head surfaces or aging gaskets.
- Engine Overheating
A damaged cylinder head or issues in the cooling system can lead to engine overheating. Prolonged overheating can further damage the cylinder head, creating a vicious cycle.
Solutions
- Inspect the Cylinder Head
Regularly check the cylinder head for cracks or other damage. If any issues are found, the cylinder head should be replaced or repaired. Ensure the sealing surface is smooth and free of defects.
- Inspect the Cooling System
Verify that the coolant flows correctly and check for leaks in the cooling system. Clean the cooling system and inspect the water pump and radiator to ensure they are functioning properly, preventing engine overheating.
- Replace the Gasket
If the cylinder head gasket is found to be aged or damaged, replace it promptly. A proper seal is crucial for the engine's optimal performance.
- Check Compression
Use a compression tester to check the compression in each cylinder. If any cylinder has low compression, it may indicate poor sealing of the cylinder head or worn valve seats, which will need further inspection and repair.
Conclusion
The Komatsu D20A-5 dozer’s cylinder head issues primarily involve damage, coolant leakage, and poor compression. By regularly inspecting the cylinder head, cooling system, and cylinder head gaskets, and addressing issues promptly, engine performance can be maintained and further damage can be prevented, ensuring optimal functionality of the dozer.
|

|
|
| CASE 530 Carrier Bearing Preload and Side Gear Issues |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:37 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Problem Overview
In the CASE 530 machine, issues related to the carrier bearing preload and side gear operation are common maintenance challenges. Many users find that improper preload settings on the carrier bearing or issues with side gears, such as abnormal noise or wear, can arise during operation. These problems not only affect the smooth functioning of the machine but could lead to more severe mechanical failures, reducing operational efficiency.
Importance of Carrier Bearing Preload
The preload on the carrier bearing is a critical factor for ensuring smooth operation and prolonging the lifespan of the machine. If the preload is too high or too low, it can lead to premature bearing wear or failure. Excessive preload creates excessive friction, which increases the mechanical load, while too little preload prevents the bearing from effectively supporting the load, causing instability in the operation.
Side Gear Issues
Side gear issues are also a common fault in the CASE 530. Wear or damage to the side gears typically causes abnormal noise in the drive system and can even affect the machine's overall performance. Common causes include inadequate lubrication, excessive wear, or improper assembly. When these issues occur, the gear mesh becomes unbalanced, leading to noise or a loss of power during operation.
How to Troubleshoot and Repair
- Check Carrier Bearing Preload
The first step is to check the carrier bearing preload to ensure it meets the manufacturer’s specifications. Both over-tightening and under-tightening the preload can affect the bearing’s lifespan and performance, so adjusting the preload within the recommended range is crucial.
- Inspect the Side Gears
Inspect the side gears for wear, visible damage, or cracks. If any issues are found, the gears should be replaced immediately. Additionally, make sure the gear system is properly lubricated to prevent rapid wear due to insufficient lubrication.
- Ensure Proper Assembly
Check the assembly of all related components, particularly the bearings, gears, and other drivetrain parts. Improper assembly can cause misalignment between components, leading to increased wear and higher chances of failure.
Conclusion
Carrier bearing preload and side gear issues in the CASE 530 are critical factors affecting machine performance and longevity. Regular inspection and maintenance of these components—ensuring proper preload on the carrier bearing, maintaining good lubrication, and monitoring side gear wear—can help prevent failures and extend the lifespan of the equipment, improving work efficiency.
|

|
|
| Using and Troubleshooting the Vibrascreen Screening Machine |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:37 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Overview of the Problem
The Vibrascreen screening machine is a crucial piece of equipment used for grading and separating materials in industries such as mining, construction, and recycling. However, problems such as insufficient vibration or poor screening performance can occur during operation. These issues can reduce productivity and lead to equipment failure, making it necessary to troubleshoot and resolve the problems promptly.
Common Issues and Causes
- Insufficient Vibration
If the Vibrascreen screening machine lacks proper vibration, it could be due to a faulty vibration motor, loose springs, or damaged cushions. Insufficient vibration will lead to uneven screening and reduced screening efficiency.
- Clogged Screens
Clogging of the screen is another common issue. Larger particles or sticky materials can easily clog the screen, resulting in reduced screening performance.
- Uneven Screening
Uneven screening can be caused by factors such as improper screen tension, material flowability, or vibration frequency. If the screen tension is too loose or too tight, it will affect the screening quality.
- Overheated or Damaged Motor
An overheated or damaged vibration motor is a major cause of insufficient vibration. Overuse or lack of lubrication can accelerate the wear of the motor, eventually causing it to fail.
Solutions
- Inspect the Vibration Motor
Regularly check that the vibration motor is operating properly, ensuring there are no unusual noises or overheating issues. If a problem is detected, repair or replace the motor as needed.
- Check the Springs and Cushions
Inspect the springs and cushions for looseness or damage. Make sure they are properly supporting the vibration function of the equipment. Tighten or replace them as necessary.
- Clean the Screen
Periodically clean the screen, especially if clogging occurs. When cleaning, be careful not to apply excessive force to avoid damaging the screen. For sticky materials, consider using a screen with larger mesh openings.
- Adjust the Screen Tension
Adjust the screen tension according to the material characteristics to ensure optimal screening performance. If necessary, reinstall or replace the screen.
- Check the Lubrication System
Ensure the lubrication system for the vibration motor and other moving parts is functioning correctly. Regularly add lubricant to reduce friction between components and extend the equipment's lifespan.
Conclusion
During operation, the Vibrascreen screening machine may experience issues such as insufficient vibration, screen clogging, or uneven screening. By regularly inspecting the vibration motor, springs, cushions, and screen, cleaning clogs promptly, adjusting screen tension, and ensuring proper lubrication, you can improve screening efficiency and extend the equipment’s operational life.
|

|
|
| The History of the First Hydraulic Excavator:Who invented the excavator? |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:36 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
The concept of using hydraulic power for more efficient digging in excavators began to take shape in the 1880s. One of the earliest attempts to incorporate hydraulic technology into excavation equipment was the 1882 excavator built by Sir W. G. Armstrong & Company in England. This machine was used in the construction of the Hull Docks. However, unlike modern excavators that use hydraulic fluid, this machine operated with water as the hydraulic fluid. Additionally, it was not a fully hydraulic machine, but a hybrid design that used cables to operate the bucket and a hydraulic cylinder to operate a set of multiplying sheaves. Unfortunately, this idea was not successful, and neither was a similar machine built in 1914 by Frank F. Armstrong for the Penn Iron Mining Company in the United States.
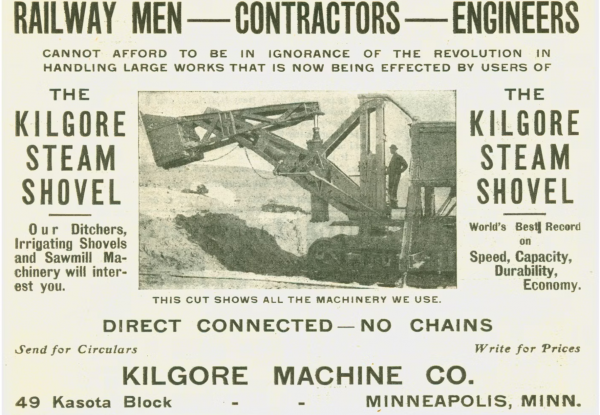
The First True Hydraulic Excavator: Kilgore's Innovation
The first all-hydraulic excavator was created by the Kilgore Machine Company in 1897. This machine, called the Direct Acting Excavator, used four direct-acting steam cylinders for all bucket functions, eliminating the need for cables or chains, which were commonly used in conventional excavators at the time. This design marked a significant breakthrough in hydraulic excavation technology.
Kilgore’s design had several notable advantages:- The excavator was made almost entirely of steel, making it robust and durable.
- All movements, including the full stroke of each cylinder, were cushioned, preventing shock or damage even when operating at high speeds and full stroke.
- The use of steam cylinders for all bucket functions provided a greater range of motion than typical cable-operated machines, allowing the bucket to crowd horizontally and manipulate larger obstacles such as boulders with greater ease.
Kilgore’s Direct Acting Excavator: Advanced Features
Kilgore’s Direct Acting Excavator was ahead of its time in many ways:- The machine had equal power in all movements, allowing the bucket to be withdrawn under load without having to lift it to the top to clear the cut, a major advantage over conventional shovels.
- In the event the shovel derailed, the machine’s design allowed for the full application of power to lift it back onto the rails, a feature not seen in traditional machines.
- The dipper could be forcefully shaken with the cylinders to dislodge materials jammed inside, improving operational efficiency.
Moreover, by eliminating complex parts such as chains, cables, sheaves, drums, friction clutches, gears, and hoisting engines, the machine’s design was simplified with fewer working parts. The operation was equally straightforward, controlled by two levers, with the engineer’s hand motion directly duplicated at the bucket. Additionally, instead of using a trip rope or lever, a foot pedal was used to dump the bucket, foreshadowing the full-revolving excavators that would emerge in the 20th century.
Kilgore’s Economic Advantage and Limited Success
Kilgore also marketed its machine’s economy of operation, noting that the cylinders required less steam, which translated into reduced fuel and water consumption compared to other traditional shovels. Moreover, the engineer operated all functions of the machine, eliminating the need for a second crew member to operate the dipper as in conventional machines.
Kilgore produced several railroad shovels with dipper capacities of 1-1/4 and 2-1/2 yards. They also created traction wheel shovels, steam ditchers for land reclamation and irrigation, and dipper dredges. Despite the advanced concepts, Kilgore’s Direct Acting Excavator met with limited success due to various factors, including competition from other established technologies and the limitations of the design at the time.
Conclusion
While Kilgore’s Direct Acting Excavator was a groundbreaking innovation in hydraulic technology, it did not achieve widespread commercial success. Nevertheless, it played an important role in the development of modern hydraulic excavators. The innovations introduced in this machine, such as cable-free operation, direct-acting cylinders, and more efficient energy use, laid the groundwork for future advancements in the field of excavation machinery.
|

|
|
| Weight of the Case 40-4 Trencher |
|
Posted by: MikePhua - 07-07-2025, 12:35 AM - Forum: Operator Talking
- No Replies
|
 |
Overview of the Issue
Many people are curious about the weight of the Case 40-4 trencher, especially when considering transportation and operation. Knowing the exact weight of the equipment is crucial for assessing stability, traction, and transportation needs.
Weight of the Case 40-4 Trencher
The standard operating weight of the Case 40-4 trencher is approximately 10,000 pounds (around 4,536 kilograms). This weight applies to the base model without additional attachments. It provides a good balance between being heavy enough to offer stability and traction, yet not so heavy as to cause transportation difficulties.
Impact of Weight on Transportation and Operation
- Transportation Requirements
The weight of the trencher is a key factor in determining the transportation method. Depending on the equipment's weight, specialized transport vehicles may be required. If the trencher exceeds certain weight limits, transport permits may be necessary, and low-boy trailers may be needed for hauling.
- Operational Stability
The weight of the trencher directly impacts its stability during operation. Heavier machines offer better traction and stability, especially in challenging terrain and when working under heavy loads. Lighter machines, while more maneuverable, may experience stability issues when handling significant weight.
Conclusion
The Case 40-4 trencher has a standard operating weight of 10,000 pounds, making it suitable for a variety of tasks. Understanding the weight of the equipment is important for transportation planning and operational stability, helping users make more informed decisions when using the trencher.
|

|
|
|