06-29-2025, 11:59 PM
The Fast Transmission is widely used in SANY’s heavy equipment, with its distinctive main and auxiliary box, dual intermediate shaft structure, and air-operated control system leaving a strong impression on users. However, properly handling air circuit failures, especially those related to the dual-H valve, can be quite challenging.
Failure Symptoms and Root Cause Analysis
When the transmission selects a low gear, compressed air passes through the low gear exhaust port of the dual-H valve and enters the low gear intake of the auxiliary shift cylinder, pushing the piston to the right. During this process, residual air in the cylinder is expelled through the high gear exhaust port of the dual-H valve, which typically produces a brief exhaust sound. This is normal. However, if the exhaust persists for too long, it can affect gear shifting, becoming a failure symptom.
It's important to note that air leakage in the dual-H valve is not due to the valve’s quality, but rather the result of poor sealing in the auxiliary shift cylinder, which causes air leakage and is reflected in the dual-H valve.
When the transmission selects a high gear, compressed air enters the high gear intake of the auxiliary shift cylinder through the high gear exhaust port of the dual-H valve, pushing the piston to the left. As this happens, residual air is expelled through the low gear port. This process also produces a short exhaust sound, but if the exhaust persists for too long, it can similarly disrupt gear shifting.

Sealing Issues and High-Low Gear Shifting Problems
The auxiliary shift cylinder uses three sealing rings to maintain a relatively sealed environment. However, as wear and tear accumulate over time, the sealing environment of the cylinder can be compromised. This leads to delays or failure to shift properly when changing between low and high gears.
In many repair situations, technicians may assume that air leakage from the dual-H valve requires a replacement of the valve itself. While changing the valve may temporarily resolve shifting issues, it does not address the root cause. The increased air pressure from a new dual-H valve may temporarily enhance the piston’s pushing force, superficially solving the gear shifting problem. However, the sealing environment of the cylinder remains unaddressed, and the issue will resurface shortly. This could lead to further damage, such as the wear or burning of the auxiliary shift cylinder.
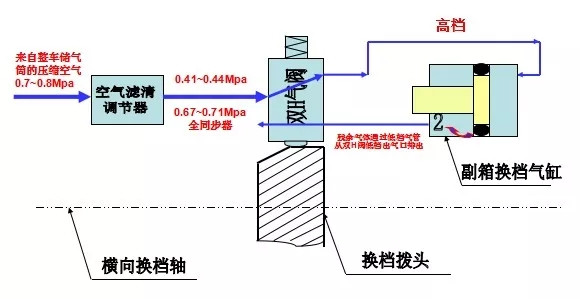
Correct Repair Method
To properly address the issue of high-low gear shifting difficulty, the first step should be to check the sealing of the auxiliary shift cylinder. Replace any failed sealing rings or repair the damaged cylinder body to restore a proper seal. Only then should other air circuit components be considered for replacement to ensure an accurate and effective resolution.
In conclusion, correctly diagnosing the root cause of air circuit failures and focusing repairs on the sealing of the auxiliary shift cylinder will help avoid recurring failures from temporary fixes, ensuring long-term reliability and stable operation of the equipment.
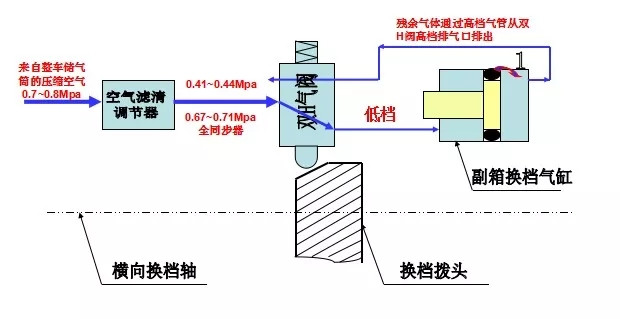
Failure Symptoms and Root Cause Analysis
When the transmission selects a low gear, compressed air passes through the low gear exhaust port of the dual-H valve and enters the low gear intake of the auxiliary shift cylinder, pushing the piston to the right. During this process, residual air in the cylinder is expelled through the high gear exhaust port of the dual-H valve, which typically produces a brief exhaust sound. This is normal. However, if the exhaust persists for too long, it can affect gear shifting, becoming a failure symptom.
It's important to note that air leakage in the dual-H valve is not due to the valve’s quality, but rather the result of poor sealing in the auxiliary shift cylinder, which causes air leakage and is reflected in the dual-H valve.
When the transmission selects a high gear, compressed air enters the high gear intake of the auxiliary shift cylinder through the high gear exhaust port of the dual-H valve, pushing the piston to the left. As this happens, residual air is expelled through the low gear port. This process also produces a short exhaust sound, but if the exhaust persists for too long, it can similarly disrupt gear shifting.
Sealing Issues and High-Low Gear Shifting Problems
The auxiliary shift cylinder uses three sealing rings to maintain a relatively sealed environment. However, as wear and tear accumulate over time, the sealing environment of the cylinder can be compromised. This leads to delays or failure to shift properly when changing between low and high gears.
In many repair situations, technicians may assume that air leakage from the dual-H valve requires a replacement of the valve itself. While changing the valve may temporarily resolve shifting issues, it does not address the root cause. The increased air pressure from a new dual-H valve may temporarily enhance the piston’s pushing force, superficially solving the gear shifting problem. However, the sealing environment of the cylinder remains unaddressed, and the issue will resurface shortly. This could lead to further damage, such as the wear or burning of the auxiliary shift cylinder.
Correct Repair Method
To properly address the issue of high-low gear shifting difficulty, the first step should be to check the sealing of the auxiliary shift cylinder. Replace any failed sealing rings or repair the damaged cylinder body to restore a proper seal. Only then should other air circuit components be considered for replacement to ensure an accurate and effective resolution.
In conclusion, correctly diagnosing the root cause of air circuit failures and focusing repairs on the sealing of the auxiliary shift cylinder will help avoid recurring failures from temporary fixes, ensuring long-term reliability and stable operation of the equipment.




